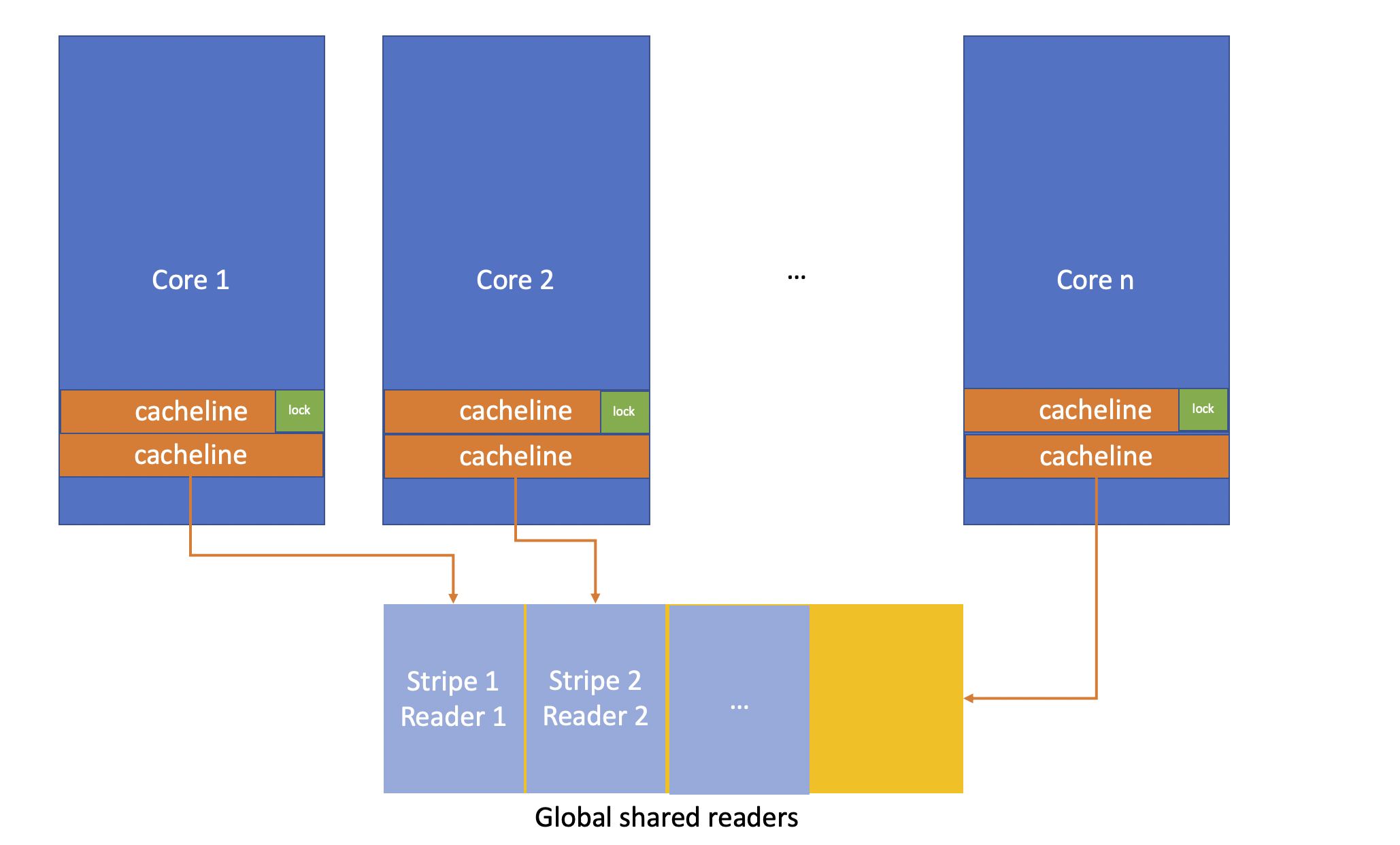
在多线程并发读写开发中,尤其是读多写少的情况,使用读写锁代替普通mutex一般可以提升读并发度。 在多个线程频繁获取和释放读锁时,read lock count计数修改会反复触发cpu cacheline同步,导致实际性能可能达不到预期。folly SharedMutex 通过将reader信息存储在全局静态区域,来减少cacheline同步。
class structure
类定义
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
using Futex = std::atomic<std::uint32_t>;
class SharedMutexImpl {
// 32 bits of state
Futex state_{};
}
|
SharedMutexImpl 仅使用32位的atomic来存储读写锁内部状态
 其中一些常用状态含义为(详见代码注释)
其中一些常用状态含义为(详见代码注释)
- kIncrHasS = 1 « 11, kHasS = ~(kIncrHasS - 1); 第11-31位表示shared lock计数, 每次增减 kIncrHasS。
- kHasE = 1 « 7; exlusive排它标志位
- kBegunE = 1 « 6; 开始获取写锁
- kHasU = 1 « 5; upgrade lock
- kMayDefer = 1 « 9; 是否有读锁信息存储在全局静态区
Global Shared readers
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
constexpr uint32_t kMaxDeferredReadersAllocated = 256 * 2;
static constexpr uint32_t kDeferredSeparationFactor = 4;
typedef Atom<uintptr_t> DeferredReaderSlot;
alignas(hardware_destructive_interference_size) static DeferredReaderSlot
deferredReaders[shared_mutex_detail::kMaxDeferredReadersAllocated
* kDeferredSeparationFactor];
|
deferredReaders定义为2048个cacheline对齐的DeferredReaderSlot,uintptr_t保存SharedMutex实例唯一的token,标记当前slot关联的SharedMutex被某个线程持有reader lock。
通过将reader lock状态保存在Global Shared readers中, 避免获取和释放读锁时反复修改state_变量。 但这样也带来一些问题:
- 申请写锁时会比一般的RWMutex慢,因为需要先保证所有相关的DeferredReaderSlot释放,再去检查和修改
state_。
- 全局静态的slot数量固定(2048个), 在读并发较高或者SharedMutex实例数足够多时,slot会不够用。这时
SharedMutex退化成普通的RWMutex,读锁申请释放还是对state_加减kIncrHasS。
实现
lock_shared
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
template <class WaitContext>
bool lockSharedImpl(Token* token, WaitContext& ctx) {
uint32_t state = state_.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);
if ((state & (kHasS | kMayDefer | kHasE)) == 0 &&
state_.compare_exchange_strong(state, state + kIncrHasS)) {
if (token != nullptr) {
token->type_ = Token::Type::INLINE_SHARED;
}
return true;
}
return lockSharedImpl(state, token, ctx);
}
|
lock_shared()主要实现在lockSharedImpl函数中, 在没有任何读写锁状态时,对state_ + kIncrHasS。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
bool lockSharedImpl(uint32_t& state, Token* token, WaitContext& ctx) {
const uint32_t maxDeferredReaders =
shared_mutex_detail::getMaxDeferredReaders();
while (true) {
if (UNLIKELY((state & kHasE) != 0) &&
!waitForZeroBits(state, kHasE, kWaitingS, ctx) && ctx.canTimeOut()) {
return false;
}
}
...
...
}
|
在lockSharedImpl的while loop中,如果写锁被占用,且等待超时直接return false.
其中waitForZeroBits实现过程大致为
- waitForZeroBits() 中先spin方式检查state kHasE状态清零,spin数到达kMaxSpinCount向下调用
- yieldWaitForZeroBits() 通过yield()方式尝试kMaxSoftYieldCount次
- futexWaitForZeroBits() 最后使用futex wait
接下来尝试获取读锁:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
|
while (true) {
if (UNLIKELY((state & kHasE) != 0) &&
!waitForZeroBits(state, kHasE, kWaitingS, ctx) && ctx.canTimeOut()) {
return false;
}
uint32_t slot = make_atomic_ref(tls_lastDeferredReaderSlot)
.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);
uintptr_t slotValue = 1; // any non-zero value will do
bool canAlreadyDefer = (state & kMayDefer) != 0;
bool aboveDeferThreshold =
(state & kHasS) >= (kNumSharedToStartDeferring - 1) * kIncrHasS;
bool drainInProgress = ReaderPriority && (state & kBegunE) != 0;
if (canAlreadyDefer || (aboveDeferThreshold && !drainInProgress)) {
/* Try using the most recent slot first. */
slotValue = deferredReader(slot)->load(std::memory_order_relaxed);
if (slotValue != 0) {
// starting point for our empty-slot search, can change after
// calling waitForZeroBits
uint32_t bestSlot =
(uint32_t)folly::AccessSpreader<Atom>::current(maxDeferredReaders);
// deferred readers are already enabled, or it is time to
// enable them if we can find a slot
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < kDeferredSearchDistance; ++i) {
slot = bestSlot ^ i;
assert(slot < maxDeferredReaders);
slotValue = deferredReader(slot)->load(std::memory_order_relaxed);
if (slotValue == 0) {
// found empty slot
make_atomic_ref(tls_lastDeferredReaderSlot)
.store(slot, std::memory_order_relaxed);
break;
}
}
}
}
if (slotValue != 0) {
// not yet deferred, or no empty slots
if (state_.compare_exchange_strong(state, state + kIncrHasS)) {
// successfully recorded the read lock inline
if (token != nullptr) {
token->type_ = Token::Type::INLINE_SHARED;
}
return true;
}
// state is updated, try again
continue;
}
// record that deferred readers might be in use if necessary
if ((state & kMayDefer) == 0) {
if (!state_.compare_exchange_strong(state, state | kMayDefer)) {
// keep going if CAS failed because somebody else set the bit
// for us
if ((state & (kHasE | kMayDefer)) != kMayDefer) {
continue;
}
}
// state = state | kMayDefer;
}
// try to use the slot
bool gotSlot = deferredReader(slot)->compare_exchange_strong(
slotValue,
token == nullptr ? tokenlessSlotValue() : tokenfulSlotValue());
// If we got the slot, we need to verify that an exclusive lock
// didn't happen since we last checked. If we didn't get the slot we
// need to recheck state_ anyway to make sure we don't waste too much
// work. It is also possible that since we checked state_ someone
// has acquired and released the write lock, clearing kMayDefer.
// Both cases are covered by looking for the readers-possible bit,
// because it is off when the exclusive lock bit is set.
state = state_.load(std::memory_order_acquire);
if (!gotSlot) {
continue;
}
...
if ((state & kMayDefer) != 0) {
assert((state & kHasE) == 0);
// success
if (token != nullptr) {
token->type_ = Token::Type::DEFERRED_SHARED;
token->slot_ = (uint16_t)slot;
}
return true;
}
// release the slot before retrying
if (token == nullptr) {
// We can't rely on slot. Token-less slot values can be freed by
// any unlock_shared(), so we need to do the full deferredReader
// search during unlock. Unlike unlock_shared(), we can't trust
// kPrevDefer here. This deferred lock isn't visible to lock()
// (that's the whole reason we're undoing it) so there might have
// subsequently been an unlock() and lock() with no intervening
// transition to deferred mode.
if (!tryUnlockTokenlessSharedDeferred()) {
unlockSharedInline();
}
} else {
if (!tryUnlockSharedDeferred(slot)) {
unlockSharedInline();
}
}
}
}
|
- 18-19行: 查找可用的Slot
- 42行: 如果没有任何读锁占用或者没有空余Slot,对
state_ + kIncrHasS。
- 55行: 找到slot时,先要置kMayDefer位
- 66-68行: slot中写入Mutex唯一的信息
- 后续检查state状态,CAS失败时释放slot,下个loop重试
unlock_shared
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
void unlock_shared() {
annotateReleased(annotate_rwlock_level::rdlock);
auto state = state_.load(std::memory_order_acquire);
// kPrevDefer can only be set if HasE or BegunE is set
assert((state & (kPrevDefer | kHasE | kBegunE)) != kPrevDefer);
// lock() strips kMayDefer immediately, but then copies it to
// kPrevDefer so we can tell if the pre-lock() lock_shared() might
// have deferred
if ((state & (kMayDefer | kPrevDefer)) == 0 ||
!tryUnlockTokenlessSharedDeferred()) {
// Matching lock_shared() couldn't have deferred, or the deferred
// lock has already been inlined by applyDeferredReaders()
unlockSharedInline();
}
}
|
12-17行: 如果锁本身没有defer状态或者当前线程没有在静态区存储S锁状态,代表之前lock_shared()时对state_ 执行了+kIncrHasS,此时进入unlockSharedInline().
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
uint32_t unlockSharedInline() {
uint32_t state = (state_ -= kIncrHasS);
assert(
(state & (kHasE | kBegunE | kMayDefer)) != 0 ||
state < state + kIncrHasS);
if ((state & kHasS) == 0) {
// Only the second half of lock() can be blocked by a non-zero
// reader count, so that's the only thing we need to wake
wakeRegisteredWaiters(state, kWaitingNotS);
}
return state;
}
|
- 2行: 执行state_ -= kIncrHasS.
- 6-10行: 如果-kIncrHasS后没有S锁状态,则唤醒等待的写锁
lock
lock()主要实现在中lockExclusiveImpl(uint32_t preconditionGoalMask, WaitContext& ctx)中,此时的preconditionGoalMask传入参数为kHasSolo = kHasE | kBegunE | kHasU
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
// Performs an exclusive lock, waiting for state_ & waitMask to be
// zero first
template <class WaitContext>
bool lockExclusiveImpl(uint32_t preconditionGoalMask, WaitContext& ctx) {
uint32_t state = state_.load(std::memory_order_acquire);
if (LIKELY(
(state & (preconditionGoalMask | kMayDefer | kHasS)) == 0 &&
state_.compare_exchange_strong(state, (state | kHasE) & ~kHasU))) {
return true;
} else {
return lockExclusiveImpl(state, preconditionGoalMask, ctx);
}
}
|
- 7-8行: 如果没有任何E锁、S锁、U锁, 则直接对state_加kHasE标志,并清空kHasU.
- 261行: 否则进入261行lockExclusiveImpl函数等待其它锁释放.
unlock
unlock实现相对简单,7行清空写标志位,第8行唤醒等待持有锁的线程。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
void unlock() {
annotateReleased(annotate_rwlock_level::wrlock);
OwnershipTrackerBase::endThreadOwnership();
// It is possible that we have a left-over kWaitingNotS if the last
// unlock_shared() that let our matching lock() complete finished
// releasing before lock()'s futexWait went to sleep. Clean it up now
auto state = (state_ &= ~(kWaitingNotS | kPrevDefer | kHasE));
assert((state & ~(kWaitingAny | kAnnotationCreated)) == 0);
wakeRegisteredWaiters(state, kWaitingE | kWaitingU | kWaitingS);
}
|
 其中一些常用状态含义为(详见代码注释)
其中一些常用状态含义为(详见代码注释)